Introduction¶
Variance reduction (VR) techniques in TOPAS can be combined to create a very sophisticated setup. However, please note that VR is highly dependent on your specific geometry. Approach these features with caution and test all variance reduced setups against an equivalent setup without variance reduction.
You should also review the Geant4 document that describes which cases are problematic here.
To enable the particle split applied to protons:
b:Vr/UseVarianceReduction = "true"
b:Vr/ParticleSplit/Active = "true"
sv:Vr/ParticleSplit/ParticleName = 1 "proton"
Specify the Split Geometry¶
The geometry for variance reduction must be in a parallel world. The type of component can be any standard solid (Dividable Components or Generic Components). The geometry must consist of a geometry component with a set of geometry sub-components as daughters. The sub-components must be located in such a way that the boundaries coincide. The split process or Russian roulette will occur at these boundaries. In the next figure a simple scheme is shown.
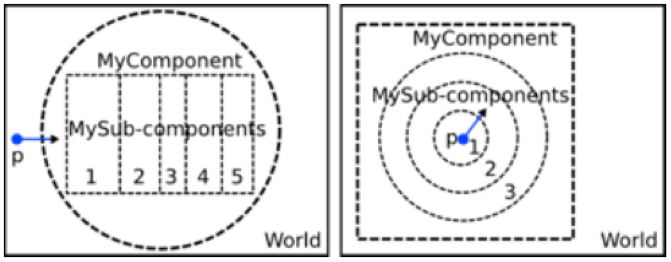
Time Features can be used to move or rotate the component or sub-components. But there is a restriction: the implementation of VR does not allow you to change the dimensions of the component and sub-components.
To set the geometry for VR:
s:Vr/ParticleSplit/Component = "MyComponent"
sv:Vr/ParticleSplit/SubComponents = n "MySubComp_1" ... "MySubComp_n"
Define the Splitting Technique¶
There are three variance reduction techniques available:
To chose a technique, use for example:
s:Vr/ParticleSplit/Type = "GeometricalParticleSplit"